How to Master Thermoforming Techniques for Optimal Results in Your Projects
In the realm of manufacturing and design, thermoforming has emerged as a pivotal technique that enables the production of intricate shapes and forms from plastic materials. This versatile process not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of products but also significantly contributes to functional efficiency in various applications. To master thermoforming techniques is to unlock a pathway to optimal results in your projects, ensuring that you can fully exploit the potential of this innovative method.
As projects become increasingly complex, the mastery of thermoforming techniques is essential for professionals seeking to elevate their work. Understanding the nuances of this process, from material selection to temperature control, is crucial for achieving high-quality results. Effective thermoforming not only streamlines production but also enhances the durability and performance of the final product. Therefore, delving deep into the methodologies and best practices of thermoforming is vital for anyone looking to make an impact in their industry.
By honing these skills and approaches, individuals can foster creativity, improve efficiency, and drive innovation in their projects. This guide aims to provide insights and practical tips on mastering thermoforming techniques, empowering you to achieve the best possible outcomes in your undertakings.

Understanding the Basics of Thermoforming Techniques
Thermoforming is a versatile manufacturing process that combines heat, pressure, and plastic to create a wide variety of products. Understanding the basics of thermoforming techniques is essential for achieving optimal results in your projects. The process typically involves heating a thermoplastic sheet until it becomes pliable, followed by forming it over a mold through vacuum or pressure application.
According to recent industry reports, the global thermoforming market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2021 to 2028, reflecting its widespread adoption across various sectors, including packaging and automotive industries.
When starting out with thermoforming, it’s crucial to pay attention to material selection. Different plastics exhibit varying characteristics when heated, which can significantly influence the final product's quality. For instance, ABS and PETG are commonly used due to their excellent thermoforming capabilities and durability. Additionally, ensuring the proper heating of the sheet is vital; overheating can lead to deformation, while underheating may result in incomplete forming.
Another essential tip is to keep your workspace clean and organized to avoid any contaminants that could compromise the quality of your thermoformed products. By mastering these foundational techniques, you can elevate the quality and efficiency of your thermoforming projects.
Essential Equipment and Materials for Thermoforming Projects
When embarking on thermoforming projects, having the right equipment and materials is crucial for achieving optimal results. The primary equipment needed includes a thermoforming machine, which can vary in size and functionality depending on the scale of your project. A heating element is essential for softening the thermoplastic sheets, while a mold, typically made from metal or high-density foam, shapes the softened material. Auxiliary tools such as a vacuum system are often used to pull the material onto the mold, ensuring a precise fit. Additionally, temperature control systems help maintain optimal heating conditions, which is key for achieving uniform results.
In terms of materials, various thermoplastics can be utilized, including ABS, polystyrene, and polycarbonate, each offering distinct properties suitable for different applications. The selection of material plays a significant role in the durability, strength, and aesthetic quality of the final product. It's also important to have a variety of finishing tools on hand, such as cutting and trimming devices, to refine the edges and surface of the formed pieces. Understanding the characteristics of both your equipment and materials will enhance the thermoforming process, ultimately leading to more successful project outcomes.
Thermoforming Techniques Efficiency Comparison
This chart illustrates the efficiency of different thermoforming techniques based on their speed and material utilization percentage. Each technique is assessed for maximum output in terms of low scrap rate and production speed.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Thermoforming Process
Thermoforming is a widely used manufacturing process that allows for the shaping of plastic sheets into various forms by heating them and then forming them over molds. The key to mastering this technique lies in understanding the step-by-step process involved. First, select the right material based on the project's requirements, as different plastics offer distinct benefits in terms of flexibility, durability, and temperature resistance. Once the material is chosen, it's essential to prepare the sheet by cutting it to the appropriate size that fits your mold.
Next, heating the plastic sheet evenly is crucial. This ensures that the material reaches a pliable state, making it easier to form over the mold without any imperfections. It’s advised to use a temperature-controlled oven for consistent results. After heating, promptly transfer the sheet onto the mold to start the forming process. Ensure that you apply adequate pressure through vacuum or pressure forming techniques to achieve the desired shape.
Tips: Always conduct a test run with a sample piece to fine-tune the temperature and pressure settings before committing to a full batch. Additionally, consider using a release agent on molds to facilitate easy removal of the formed plastic. Take notes on the process variations, as each project may require slight adjustments to achieve optimal results.
How to Master Thermoforming Techniques for Optimal Results in Your Projects
| Step | Technique | Material Used | Temperature Range (°F) | Time (Seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Heating | Polypropylene (PP) | 350-400 | 30-60 |
| 2 | Forming | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | 290-350 | 20-40 |
| 3 | Cooling | Polystyrene (PS) | Ambient | 60-120 |
| 4 | Trimming | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Ambient | 10-20 |
| 5 | Finishing | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Room Temperature | 10-15 |
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Thermoforming
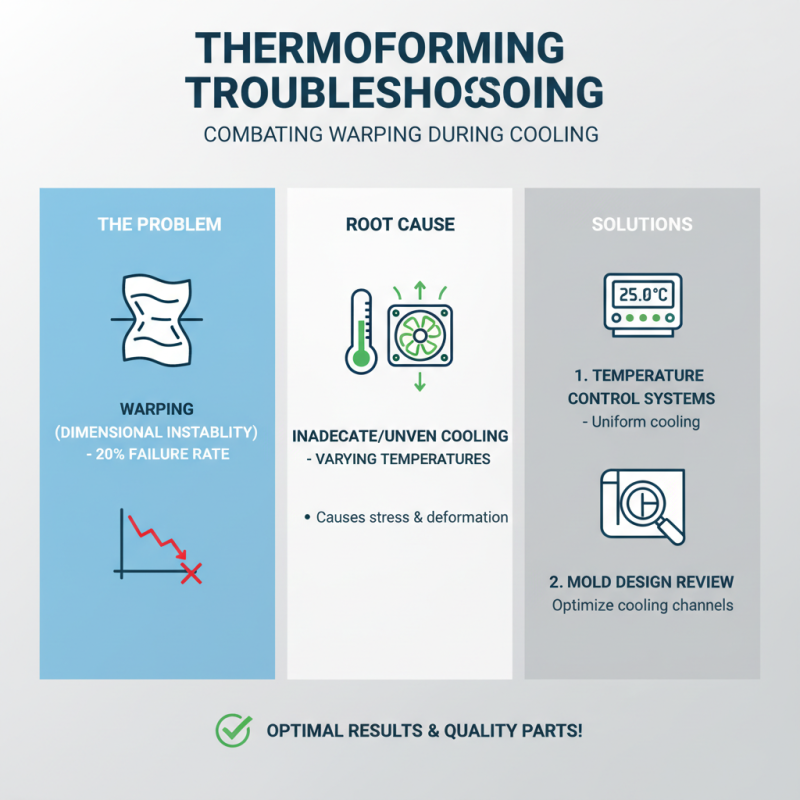
Troubleshooting common issues in thermoforming is vital for achieving optimal results in your projects. One prevalent problem is warping during the cooling process. According to a recent industry report, about 20% of thermoformed parts fail quality checks due to dimensional instability caused by inadequate cooling. Ensuring uniform cooling across the formed shapes can mitigate this issue. Utilizing temperature control systems and conducting thorough mold design reviews can help maintain consistent cooling rates.
Another common challenge is air entrapment, which often leads to surface defects. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) states that incorrect vacuum pressure can result in 25% of defective parts. To avoid this, it's crucial to optimize the vacuum system setup and conduct routine maintenance checks. Ensuring proper venting in the molds not only helps in reducing air pockets but also enhances the overall quality of the finished product.
Tips:
1. Regularly calibrate your thermoforming machines to ensure they are operating at optimal parameters.
2. Conduct trial runs with smaller batches to identify potential issues before full-scale production.
3. Invest in high-quality materials that are less prone to warping and deformation during the forming process.
Tips for Achieving Optimal Results in Thermoforming
Achieving optimal results in thermoforming requires a combination of technical knowledge and hands-on experience. One of the most important aspects is selecting the right materials. Understanding the properties of different thermoplastics is crucial, as their behavior under heat varies significantly. For instance, materials with lower heat distortion temperatures can lead to issues during forming. It's essential to conduct material tests to determine the best choice for your specific project, ensuring that the product maintains integrity and functionality after the process.
Another key factor is controlling the heating process. The temperature must be precisely managed to ensure even heating of the plastic sheet, as overheating can lead to deformities or burning, while insufficient heating may prevent proper forming. Utilizing specialized ovens or heating equipment designed for thermoforming can enhance consistency. Additionally, the use of appropriate molds is vital; they should be constructed to facilitate even pressure distribution and minimize air entrapment, which can compromise the final product quality.
Properly cooling the formed parts is also critical, allowing them to retain their shape and strength post-forming. By focusing on these aspects, you can significantly improve the outcomes of your thermoforming projects.
Related Posts
-

Top 7 Benefits of Using Thermoforming Plastic in Modern Manufacturing
-

Crafting Excellence: China’s Finest Thermoformed Trays for Global Markets
-

Unlocking the Secrets of the Thermoforming Process: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
-

Revolutionizing Spill Management The Definitive Guide to the Best Spill Tray Innovations by 2025
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Industrial Drip Tray for Your Business Needs
-

Top 5 Plastic Vacuum Forming Machines You Need to Know in 2023 for Optimal Production