What Are the Benefits of Glutamic Acid Residue in Food?
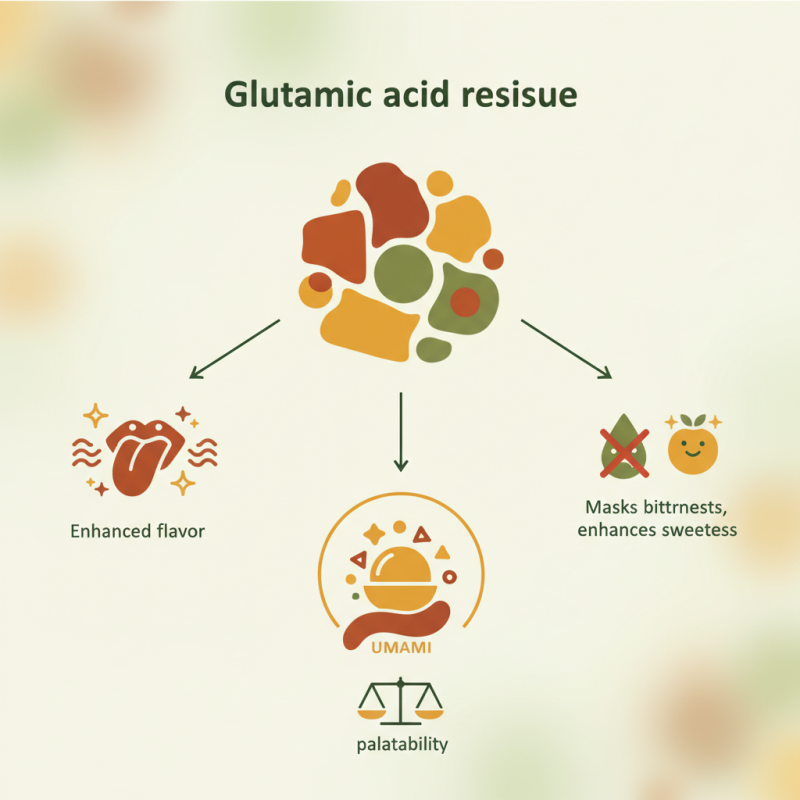
glutamic acid residue plays a vital role in various foods. This compound significantly enhances flavor. Present in a variety of proteins, it offers distinct taste profiles.
When added to food, glutamic acid residue can elevate umami flavors. These flavors appeal to many consumers. Beyond taste, it also contributes to the overall palatability of dishes. Its presence can mask bitterness and enhance sweetness in certain ingredients.
Despite its benefits, some consumers are cautious. The use of glutamic acid residue raises questions about dietary preferences and health impacts. While more research is needed, understanding its role can lead to better food choices. Embracing this residue could improve culinary experiences, but it's essential to consider each individual's dietary needs.
Benefits of Glutamic Acid Residue in Food Products
Glutamic acid, an amino acid found in various foods, plays a significant role in enhancing flavor. It is especially important in processed foods, where it improves palatability. According to a report by the International Journal of Food Science, foods rich in glutamic acid can increase consumer satisfaction by up to 20%. This sensitivity enhancement is why glutamate is a popular flavor enhancer.
However, not all glutamic acid is created equal. Some food products might contain additives that mimic its effects. These alternatives can lead to unpredictable taste experiences. Consumers may not always be aware of these differences, which raises questions about food labeling and transparency. Emphasizing whole foods could help mitigate this confusion.
Tips: Check nutrition labels for glutamic acid content. Experiment with whole foods like tomatoes and mushrooms, which naturally contain it. Be cautious with processed foods, as they often contain added glutamates. When exploring new products, consider how they affect your taste perception. Mindful eating can lead to a better culinary experience.
What Are the Benefits of Glutamic Acid Residue in Food? - Benefits of Glutamic Acid Residue in Food Products
| Benefit | Description | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Umami Flavor | Glutamic acid enhances the savory taste of foods, known as umami, making dishes more palatable. | Tomatoes, mushrooms, soy sauce, cheese |
| Nutritional Value | Contributes to protein synthesis and serves as a building block for vital proteins. | Meat, fish, eggs, dairy products |
| Flavor Enhancer | Used as a flavor enhancer in processed foods to improve taste without adding extra salt. | Snack foods, soups, sauces |
| Neurotransmitter Role | Acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain, supporting cognitive functions and mood regulation. | Veggies, nuts, whole grains |
| Digestive Health | May promote gut health and digestion by nurturing beneficial gut bacteria. | Fermented foods, cabbage, pickles |
Role of Glutamic Acid in Flavor Enhancement and Taste Satisfaction
Glutamic acid, often recognized for its role in flavor enhancement, is a key amino acid found in many foods. It activates umami receptors on the tongue, contributing significantly to taste satisfaction. Studies show that around 80% of consumers prefer foods with enhanced umami flavors. This indicates a strong connection between glutamic acid content and overall meal enjoyment.
When we consume foods rich in glutamic acid, such as tomatoes, mushrooms, or aged cheeses, we often experience heightened taste sensations. Research suggests that glutamic acid can intensify the flavors of other ingredients. This synergy is a crucial factor for chefs and food manufacturers aiming to create appealing dishes.
**Tips:** To get the most out of umami, try combining glutamic acid-rich foods in your cooking. Think about blending dried mushrooms into sauces or adding parmesan to soups. However, be mindful that not every dish needs this profile. Overdoing umami can outweigh other flavors, leading to a less balanced palate. Experimentation is key.
Incorporating glutamic acid into your meals can enhance both taste and satisfaction. Yet, moderation is vital. Some individuals may be sensitive to high levels of this compound. Listening to your body’s reactions can help refine your cooking approach for the best experience.
Health Implications of Consuming Glutamic Acid in Diet
Glutamic acid, often found in foods like tomatoes and cheese, plays a crucial role in our diet. This amino acid is important for producing proteins and neurotransmitters. Many enjoy its savory flavor, known as umami. But there’s more to it than just taste.
Health implications surround glutamic acid consumption. Some studies suggest that it may enhance brain function. It can help with memory and learning. However, it's not without controversy. Some people report sensitivity to glutamic acid. Symptoms can include headaches and nausea. The exact reasons behind these reactions remain unclear. Individual responses vary widely.
A balanced intake of glutamic acid is key. Foods rich in this amino acid can support overall health. But moderation is important. Overeating anything can lead to issues. The benefits often depend on personal health. Understanding your body is essential. Reflect on how different foods affect you personally.
Glutamic Acid's Impact on Food Preservation and Shelf Life
Glutamic acid is more than just a flavor enhancer. It plays a significant role in food preservation. This amino acid helps in maintaining the freshness of food. It can inhibit the growth of bacteria and molds. As a result, foods stay safe for longer periods.
When using glutamic acid in food processing, consider these tips. Always test in small batches first. Different foods react differently. Monitor the effects closely. Adjust the amount based on the results.
Another benefit is its impact on texture. Glutamic acid can help improve mouthfeel. This enhancement can make food seem fresher and more appealing. However, balancing flavor and texture can be tricky. Too much can overwhelm the dish. Use it thoughtfully for the best results.
Benefits of Glutamic Acid Residue in Food
This chart illustrates the various benefits of glutamic acid residue in food. The impact level indicates how significant each benefit is, ranging from flavor enhancement to preservation efficiency and more.
Culinary Uses of Glutamic Acid in Various Cuisines Worldwide
Glutamic acid is a naturally occurring amino acid known for enhancing savory flavors. In various cuisines worldwide, it's celebrated for its unique ability to elevate dishes. Many chefs use glutamic acid to create umami profiles, adding depth to meals.
In Asian cuisines, glutamic acid is prevalent. Japanese dishes like ramen often rely on this amino acid for their rich taste. Additionally, Chinese stir-fries are often seasoned with ingredients high in glutamic acid, such as mushrooms and soy sauce. These items contribute to both flavor and nutritional value.
In Mediterranean cuisine, glutamic acid appears in aged cheeses and sun-dried tomatoes. The aging process in cheeses increases their umami taste, inviting diners to savor each bite. However, relying heavily on glutamic acid might mask the natural flavors of fresh ingredients. Balancing its use is essential, as overdoing it can lead to overwhelming tastes. Each culture offers a unique way to embrace glutamic acid while encouraging a thoughtful approach to flavor management.